negative angle of rotation in polarimeter|polarimetry pdf : member club A polarimeter is an instrument which measures the angle of rotation by passing polarized light through an optically active (chiral) substance. To measure optical rotation, a Light Emitting Diode (LED) produces a beam of ordinary light. WEBt. e. Kunihiko Ikuhara (幾原 邦彦, Ikuhara Kunihiko, born December 21, 1964), also known by the nickname Ikuni, is a Japanese director, writer, artist, and music producer. He has created and collaborated on several notable anime and manga series, including Sailor Moon, Revolutionary Girl Utena, Penguindrum, Yurikuma Arashi, and Sarazanmai .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Vera & John the fun place to be, Try your favorite games acro.
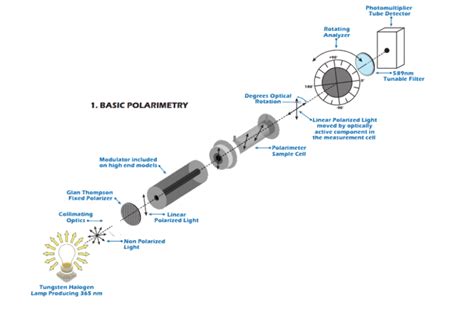
An analyzer is the component of a polarimeter that allows the angle of rotation of plane-polarized light to be determined. Specific rotations are normally measured at 20°C, and this property may be indicated by the symbol \([\alpha]^{20}_{D}\).
For clockwise direction, the rotation (in degrees) is defined as positive ("+") and .Specific rotation equation, [α], is a fundamental property of chiral substances that is expressed as the angle to which the material causes polarized light to rotate at a particular temperature, wavelength, and concentration. The term for specific .
A polarimeter is a scientific instrument used to measure optical rotation: the angle of rotation caused by passing linearly polarized light through an optically active substance. Some chemical substances are optically active, and linearly polarized (uni-directional) light will rotate either to the left (counter-clockwise) or right (clockw.
A polarimeter is an instrument which measures the angle of rotation by passing polarized light through an optically active (chiral) substance. To measure optical rotation, a Light Emitting Diode (LED) produces a beam of ordinary light. The longer the path of light through a solution of molecules, the more molecules will be encountered by the light, and the greater the optical rotation. The value of the optical . In this article, we will explore how a polarimeter works and its various applications in different fields. How Does a Polarimeter Work? A polarimeter works on the principle of .α is the measured angle of rotation of the polarized light plane (°), w is the concentration of the dissolved compound (the mass fraction of the dissolved substance) (%), . ρ is the density of .
If zero on the inner scale sits below zero on the outer scale, this means you have a sugar that has a negative degree of rotation. To complete this reading, take the number you obtain and subtract it from 180 degrees or just note the negative .How Does It Work? Malus’s Law. The resultant intensity (I) of plane-polarized light passing through two polarizers is proportional to the product between cos2 of the angle between their .
The specific rotation of a pure substance is an intrinsic property. In solution, the formula for specific rotation is: \[ [\alpha]^T_\lambda = \dfrac{\alpha}{I\cdot c}\] where [α] is the specific rotation in degrees cm 3 dm .
polarimetry vs optical rotation
polarimetry specific rotation equation
Mooney viscosity—PC type agency
Optical rotation, also known as polarization rotation or circular birefringence, is the rotation of the orientation of the plane of polarization about the optical axis of linearly polarized light as it travels through certain materials. Circular birefringence and circular dichroism are the manifestations of optical activity.Optical activity occurs only in chiral materials, those lacking . Measurement of Optical Rotation . Polarimeter is the instrument that measures the direction and angles of rotation of plane-polarized light. The plane-polarized light pass through the sample tube containing the solution of .Explanation: A polarimeter is a scientific instrument used to measure the angle of rotation caused by passing polarized light through an optically active substance. 2. A solution of 0.1 g/mL of a pure R enantiomer in a 1.0 dm (i.e., 10 cm) polarimeter rotates plane polarized light by +4.8°.
A polarimeter is an optical instrument with which one can accurately measure the angle by which the polarization of light is rotated e.g. when it passes through an optically active medium (containing chiral molecules).. Operation Principle of Polarimeters. The basic operation principle of a polarimeter comprises the following:An analyzer is the component of a polarimeter that allows the angle of rotation of plane-polarized light to be determined. . If the sample concentration is reduced by 10%, then the positive rotation would change to +81º (or +243º) while the negative rotation would change to –81º, and the correct α would be identified unambiguously. .Polarimetry is the measurement of optical rotation of substances by using a polarimeter. A polarimeter is an instrument which measures the angle of rotation by passing polarized light through an optically active (chiral) substance. To measure optical rotation, a Light Emitting Diode (LED) produces a beam of ordinary light.
Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\): The effect of path length on optical rotation. The longer the path of light through a solution of molecules, the more molecules will be encountered by the light, and the greater the optical rotation. The value of the optical rotation must be corrected for the length of the cell used to hold the sample.An analyzer is the component of a polarimeter that allows the angle of rotation of plane-polarized light to be determined. . If the sample concentration is reduced by 10%, then the positive rotation would change to +81º (or +243º) while the negative rotation would change to –81º, and the correct α would be identified unambiguously. .
The plane of polarization can be determined by an instrument called a polarimeter, . direction, and the analyzer must be turned an appropriate matching angle, . (or +243º) while the negative rotation would change to –81º, and the correct α .
Recording optical rotation with a polarimeter: The plane of polarisation of plane polarised light (4) rotates (6) as it passes through an optically active sample (5).This angle is determined with a rotatable polarizing filter (7).. In chemistry, specific rotation ([α]) is a property of a chiral chemical compound. [1]: 244 It is defined as the change in orientation of monochromatic plane .Turn on the polarimeter and allow it to warm up for 30 minutes. Fill the polarimeter cell with a solvent that has a known specific rotation value. Place the cell in the polarimeter and adjust the polarimeter until the reading matches the known specific rotation value of the solvent. Repeat the process with the same solvent to ensure accuracy.The polarimeter measures the rotation of plane polarized light caused by a solution containing an optically active compound. . -glucose) is biologically active. The amount of rotation is defined as the rotation angle. The rotation angle depends on (1) the nature of the solution, (2) the concentration of the solution, (3) the duration of the .
Ask the Chatbot a Question Ask the Chatbot a Question polarimetry, in analytic chemistry, measurement of the angle of rotation of the plane of polarized light (that is, a beam of light in which the vibrations of the electromagnetic waves are confined to one plane) that results upon its passage through certain transparent materials. Polarimetry is of interest to the chemist .Their primary use is to measure the angle of rotation of an optically active substance using polarized light. The polarized light will either rotate clockwise or counter-clockwise and the amount it rotates indicates the angle of rotation. .Polarization measurements as a function of solar phase angle for atmosphereless bodies are negative at low phase angles; comparisons with laboratory measurements indicate this is characteristic of complex, porous surfaces consisting of multisized particles. . The degree of rotation observed in a polarimeter, . (ϕ)/I 3 (ϕ) of the second . Analyzer: Measures the angle of rotation after the polarized light passes through the sample. Scale or Digital Display: Displays the measured angle of optical rotation. Types of Polarimeters. There are several types of polarimeters: Manual Polarimeters: Require the user to manually adjust the analyzer to determine the angle of rotation.
I understand that in a polarimeter, light passes through a filter that converts it into plane . Skip to main content. . Surely after a 90 degrees rotation, the angle would be the same as another angle is we'd rotated in the opposite direction. For example, I could say that a +100 degrees rotation is the same as a -10 degrees rotation .
measure the rotation angle using the following formula (Top cup mark – Bottom cup mark). If you rotated the cup in the positive direction (clockwise) this value should be positive, if you rotated in the negative direction (counterclockwise) the value should be negative. Figure 4: Polarimeter calibration and QR-Code for the single light sourceThe observed specific rotation is determined by us and is only for our experimental purposes, unlike the specific rotation which is a constant literature value. For example, let’s say we synthesized (S)-2-bromobutane and measured the optical rotation of the sample in a 10.0 cm tube and it appears to be +2.70 o.
Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\): The effect of path length on optical rotation. The longer the path of light through a solution of molecules, the more molecules will be encountered by the light, and the greater the optical rotation. The value of the optical rotation must be corrected for the length of the cell used to hold the sample. Optical rotation in a clockwise direction (as viewed towards the light source) is defined as dextrorotation (+) and the opposite, levorotation (-). The angle of rotated plane of polarization is called optical rotation and a polarimeter is used instrument to measure the degree of optical rotation.
The side is then rotated by an angle θ in an anticlockwise direction such that its final side is OA. Here, ∠AOB formed is a positive angle. What is a Negative Angle. An angle formed by a clockwise rotation from its initial side is called a negative angle. Thus -9°, -45°, -110°, -280°, -310° are all example of negative angles.
8. To determine the observed angle of rotation for the optically active sample (α), subtract the blank’s angle of maximum illumination (Step 3) from the angle of maximum illumination for the sample (Step 6). 9. A compound will consistently have the same specific rotation under identical experimental conditions.If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked. However, different low quantity organic components in honey with large positive or negative rotation angles could significantly contribute to its specific rotation. It has been observed that a number of honeydew honeys are dextrorotatory, . Measurement of angular rotation (α D) was performed at 20 °C on a Jasco P-2000 polarimeter .
In the specific rotation equation, one can note that the units that must be used have been explicitly mentioned, i.e. the angle of observed rotation must be mentioned in degrees, the length of the .
Rubber Brittleness Tester agency
polarimetry pdf
WEBInscreva-se para ganhar dinheiro interagindo com seus fãs! Compartilhe conteúdo exclusivo.
negative angle of rotation in polarimeter|polarimetry pdf